Gone are the days when you needed to buy physical hardware, connect them all to your local network at your workplace; build a new data center to expand your company in a new geographical location. Today, in the vast expanse of the digital universe, you can access your data from anywhere in the cloud.
Not from the place where rainbows emerge, but a network of digital wonders that has revolutionized the way in which we store and share data; and interact with each other digitally.
In cloud computing, the cloud refers to a network of remote servers hosted on the internet that store, manage and process data and applications instead of relying on local servers or personal computers. This allows users to access and use computing resources and services on-demand, over the internet, without the need for owning and maintaining physical hardware and software.
Now coming back to our question: How secure is the cloud?
Imagine this scenario: You are storing all your precious stuff in a particular safe at home. Yes, it is locked. You fix CCTVs, have guards and alarms. But is it really secure? Can't a burglar bypass all this? What happens in the case of a natural disaster?
Now, imagine storing all this in a highly secure place provided by a company. The company has thousands of clients and it specializes in storage and security. Employees regularly update the environment to fix any loopholes with regular security scans. You have multiple copies of the same thing- everything is backed up. Your stuff is not at home, but you can access it remotely on demand if you have the password.
This is the level of security the cloud provides. So, it is definitely more secure than local storage methods.
Data on the cloud is secured through a combination of technical and organizational measures designed to protect it from unauthorized access, data breaches and other security threats.
The following are some common measures taken by cloud providers to keep your data secure:
1. Encryption
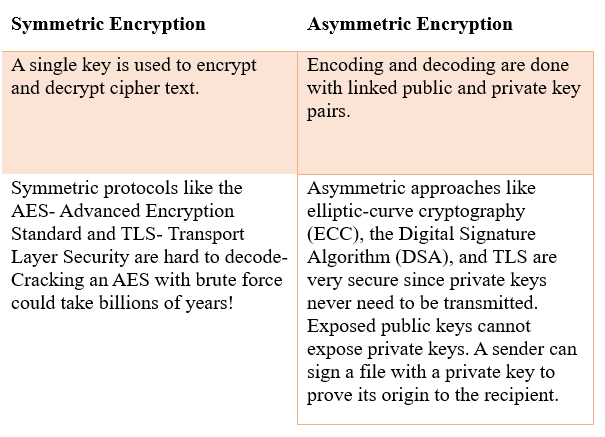
All cloud encryption protocols fall into two major categories: Symmetric and Asymmetric encryption.
These encryption techniques are used to encrypt the data stored in the cloud.
The data in transit is encrypted as it travels between your device and the cloud server using HTTPS or SSL for web traffic or VPNs for private networks. Even if someone gains physical access to the servers, the data remains unreadable without the encryption keys.
2. Access Management
Access management in cloud security is the process of controlling and regulating who has access to cloud resources, data and services within a cloud environment. This is crucial to ensure that only authorized individuals and systems can interact and access data. Some types of access management include:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) : It involves managing user identities, roles and permissions- users are assigned unique identities like usernames or email addresses. They are then granted specific permissions based on roles or responsibilities.
- Multi- Factor Authentication (MFA) : It creates an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verifications to access their accounts. This can be a hardware token, One Time Password etc.
- Just In Time Access (JIT) : Allows access to users only for a specified period when they need it and automatically revokes access once the need expires.
3. Monitoring and Logging
Access logging and monitoring mechanisms are used to track and review user activities within the cloud. Unusual actions are detected and can be investigated.
4. Data Backups
Cloud services replicate data across multiple data centers and regions ensuring high speed data availability and redundancy. Data is regularly or even automatically backed up to prevent data loss due to hardware failures.
5. Penetration Testing
Cloud providers regularly conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify and address weaknesses.
The user's role in cloud security:
While the cloud service providers are responsible for securing their infrastructure, we play an equally important role in securing our data. Here are some tips for the same:
- Use strong, unique passwords for accounts. Enable multifactor authentication.
- Classify your data based on importance and sensitivity. Apply appropriate access controls and provide the least privileges required for every user in the shared cloud environment to reduce the risk of excessive access.
- Ensure that the device used to access the cloud is secure. Use the latest antivirus and anti-malware software.
- Monitor user activity regularly for any suspicious activity.
- Review the security policies of any third-party application you use in the cloud.
- Educate the users in the cloud about the best security practices.








0 Comments