Welcome to our comprehensive journey into the fascinating world of DNS (Domain Name System)! As the unsung hero of the internet, DNS plays a crucial role in translating human-readable domain names into their corresponding IP addresses. In this blog post, we will dive deep into the inner workings of DNS, exploring its intricate layers and shedding light on its remarkable architecture. Get ready for an exciting adventure as we decode the mechanisms that make the internet's address book tick!
What is DNS ?
Domain Name System, or DNS, is an essential technology that makes it possible to convert human-readable domain names, such as "www.google.com," into the numerical IP addresses that computers use to identify and communicate with one another on the internet. To ensure that readers can access a blog by entering its domain name in a web browser, DNS is essential in the context of blogs.
In simple terms DNS is like a phone book of the Internet .Each Internet-connected device has a distinct IP address that other computers can use to find the device. DNS servers take the place of the necessity for people to remember IP addresses like 192.168.1.1 (in IPv4) or more complicated modern alphanumeric IP addresses like 2400:cb00:2048:1::c629:d7a2 (in IPv6).
Why DNS ?
The DNS (Domain Name System) is a vital part of the internet's architecture and performs a number of significant tasks. To create a human-readable name system for the internet is one of its main purposes. Users can just type in well-known domain names like "www.google.com" into their web browsers to access websites rather than having to memorize and enter numeric IP addresses. In order to facilitate seamless communication between computers and servers, DNS serves as a bridge between these domain names and the appropriate IP addresses.
The DNS Resolution Process: A Step-by-Step Exploration
Requesting a Resolution:
When you enter a URL like "www.example.com" in your web browser, your computer initiates the DNS resolution process by sending a request to a DNS server. This DNS server is typically provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). The request asks the DNS server to find the IP address associated with the domain name "www.example.com."
Recursive Lookup: The DNS Detective:
If the DNS server doesn't have the IP address in its cache, it becomes a DNS detective. It performs a recursive lookup by reaching out to other DNS servers to find the desired IP address. The DNS server acts as an intermediary, forwarding the request until it reaches a server that has the necessary information.
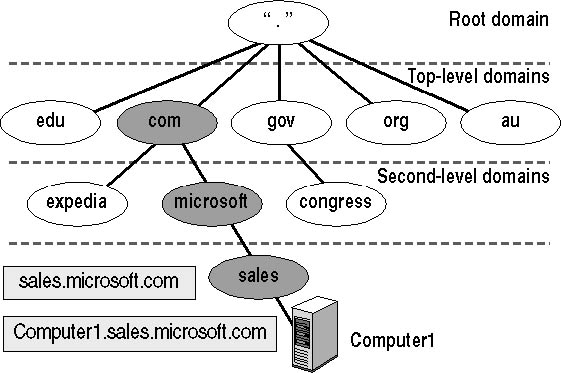
The Root DNS Server: The Foundation of the Hierarchy:
During the recursive lookup, the request eventually reaches the root DNS server. The root DNS server is the foundation of the DNS hierarchy and holds information about the IP addresses of all the top-level domain (TLD) servers. It doesn't store information about specific domain names but provides directions on how to reach the appropriate TLD server.
TLD Servers: Directing the Way:
Using the information from the root DNS server, the DNS server handling the recursive lookup is directed to the appropriate TLD server based on the domain's extension. For example, if the domain is "example.com," the DNS server is guided to the TLD server responsible for the ".com" extension. TLD servers manage specific top-level domains like ".com," ".org," ".edu," and more.
Authoritative DNS Server: The Source of Truth:
The TLD server then passes the request to the authoritative DNS server responsible for the specific domain, such as "example.com." The authoritative DNS server is the ultimate source of truth for the domain and possesses the most up-to-date information, including the IP address associated with the domain.
Returning the IP Address: Mission Accomplished!
Once the authoritative DNS server retrieves the IP address associated with the requested domain, it sends the IP address back through the chain of DNS servers involved in the resolution process. The IP address finally reaches your computer, allowing your web browser to establish a connection with the desired web server and load the website.
Now, let's delve into the hierarchical structure of DNS:
The Root Level: The Guardians of the Internet:
At the root level, a distributed network of root servers exists as the guardians of the internet. These servers are spread across different locations worldwide and collectively hold the IP addresses of all the TLD servers. Their primary function is to ensure the stability and reliability of the DNS system by maintaining this crucial information.
The TLD Level: Gatekeepers of Domain Extensions:
TLD servers manage specific top-level domains. They are responsible for storing the necessary information to direct DNS queries towards the authoritative DNS servers responsible for the respective domains. For example, if a DNS query is for a domain with the ".com" extension, the TLD server for ".com" handles the request and provides the appropriate directions to reach the authoritative DNS server for that domain.
The Domain Level: Navigating the Digital Landscape:
At the domain level, domain servers come into play. These servers handle requests for specific domain names, such as "example.com" or "example.org." When a DNS query arrives at a domain server, it redirects the request to the corresponding authoritative DNS server, where the domain's IP address resides. The domain server acts as a middleman, efficiently navigating the digital landscape by routing the request to the correct authoritative DNS server.
The hierarchical structure of DNS ensures efficient and reliable resolution of domain names to their corresponding IP addresses, enabling smooth internet connectivity
Congratulations! You've successfully unraveled the intricate inner workings of DNS. From the recursive lookup process to the hierarchical structure, DNS ensures that our web browsing experience remains seamless. It acts as a reliable guide, effortlessly translating domain names into their respective IP addresses. As you navigate the internet, remember the vital role played by DNS in connecting you to the websites and resources you love. Let's raise a virtual toast to the magic happening behind the scenes, thanks to the incredible world of DNS.
Connect with me on LinkedIn






0 Comments